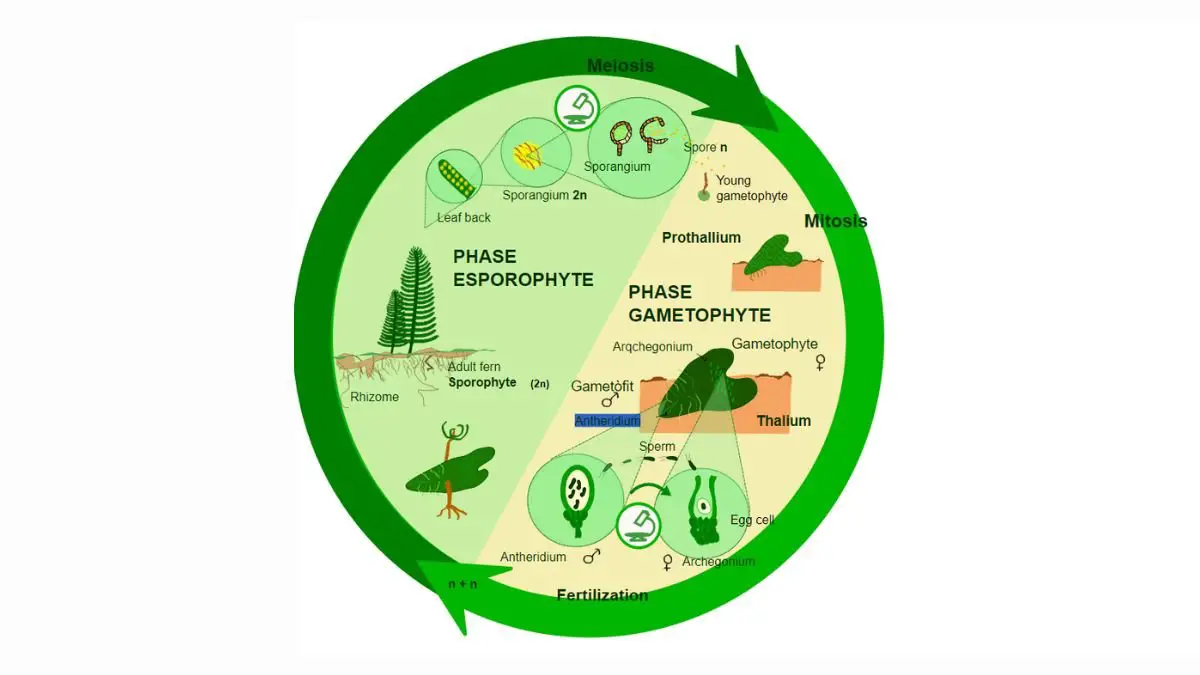
If you're curious about "Where do fern antheridia develop?", Unlike flowering plants, ferns have a unique life cycle that involves two distinct generations: a spore-producing sporophyte (the leafy fern plant we see) and a gamete-producing gametophyte. Figuring out where fern antheridia develop is key to understanding this fascinating process.
The antheridia are responsible for producing sperm. These sperm are released from the antheridia and swim through free water towards the archegonia, the female sex organs, which release simple organic acids. This process is facilitated by the unique structure of the sperm, which are almost entirely made up of nuclear material but have spiral bands of cilia on their surface to enable locomotion. The fertilization process culminates with the sperm penetrating the egg located within the archegonium.
This is just the first step in the fern's reproductive journey. If you're curious about how the antheridia display and produce sperm, and how fertilization occurs, there's much more to look and explore in the fascinating world of fern reproduction!
Key Takeaways
- Understanding Fern Reproduction is essential to grasp the intricacies of fern antheridia development.
- Ferns develop antheridia as part of their reproductive process, contributing to successful fertilization.
- Antheridia play a crucial role in the fertilization process of ferns by producing sperm cells.
- The fertilization process in ferns involves the fusion of sperm cells from antheridia with egg cells to form a zygote.
- Environmental factors significantly influence the lifecycle and reproductive strategies of ferns.
- Conservation efforts are vital to protect the diverse and adaptive reproductive mechanisms of ferns.
Understanding Fern Reproduction
Gametophyte Role
The gametophyte is responsible for producing antheridia and archegonia, serving as the reproductive structure in ferns. It offers a platform for fertilization to occur successfully.
Antheridia Function
Antheridia contain numerous sperm cells, developing on the underside of the prothallus. They play a crucial role in the overall process of fern reproduction.
Archegonia Importance
Archegonia house the egg cell and are typically located near the antheridia on the prothallus. They are essential for facilitating the fertilization process.
Fern Antheridia Development
Location on Gametophyte
Antheridia are found on the underside of the prothallus, while archegonia are commonly located nearby. This positioning is crucial for facilitating successful fertilization within ferns. The proximity of antheridia and archegonia enhances the chances of reproductive success.
Fern gametophytes undergo a series of growth stages, progressing from spores to fully developed structures. At specific points in this growth process, antheridia and archegonia begin to form. These critical growth stages are essential for the successful reproduction of ferns.
Growth Stages
Nutrients, light exposure, competition with other plants, and the presence of antheridiogens all play significant roles in influencing the development of antheridia in ferns. An environment with limited nutrients and increased competition tends to promote the production of antheridia. These external factors actively shape the characteristics of fern gametophytes.
Environmental conditions such as nutrient availability, light intensity, competition for resources, and the presence of chemical signals known as antheridiogens directly impact the development of antheridia in ferns. A scarcity of nutrients combined with heightened competition typically favors the production of antheridia over archegonia. The interplay between these environmental factors significantly influences fern reproduction.
The Role of Antheridia
Sperm Cells Production
Antheridia contain numerous sperm cells crucial for fertilizing the egg, contributing to fern reproduction. Sperm production occurs within the antheridium, ensuring the continuation of the fern life cycle.
Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity arises from the fusion of sperm and egg cells, a process facilitated by antheridia in ferns. These structures play a vital role in contributing to genetic variability, essential for species survival and adaptation.
Fertilization Process in Ferns
Sperm to Egg Journey
Sperm cells travel from antheridia to archegonia, navigating the prothallus structure for fertilization. This journey is crucial for successful reproduction in ferns.
The interaction between sperm and egg cells is critical for the fertilization process to occur. The sperm must reach the egg within the archegonium to initiate fertilization.
Conditions for Fertilization
Specific conditions are required for successful fertilization in ferns. The presence of water is essential as it helps sperm cells swim to the archegonium.
Proper environmental factors, such as moisture and temperature, play a vital role in enhancing the chances of successful fertilization. These factors create an ideal setting for the sperm-to-egg interaction.
The Lifecycle of Ferns
From Spore to Gametophyte
Fern life cycle initiates with spore germination. These spores then develop into a gametophyte, which contains antheridia and archegonia. This transition signifies the beginning of the fern's reproductive process.
Transition to Sporophyte
Successful fertilization results in the development of the sporophyte stage. The sporophyte represents the subsequent phase in the fern life cycle. This transition is crucial for fern propagation.
Environmental Influence
Moisture Requirement
Moisture essential for fern gametophyte survival. Antheridia and archegonia function optimally in moist environments. Lack of moisture can hinder fertilization process.
Light and Shade Impact
Light influences gametophyte growth and development. Antheridia and archegonia respond to light conditions. Shade can affect reproductive success in ferns.
Adaptive Strategies of Ferns
Circinate Vernation
Circinate vernation refers to the unique unfurling pattern of fern fronds, crucial for their growth and development. This process is intricately linked to fern reproduction, where the formation of antheridia and archegonia coincides with circinate vernation. These structures are essential for the production of reproductive cells in ferns.
i, which are clusters of sporangia containing spores necessary for fern reproduction, play a vital role in the life cycle of ferns. The development of sori involves the contribution of antheridia and archegonia, which aid in the formation of sporangia within these structures. Understanding sori formation is key to comprehending the reproductive strategies employed by ferns to ensure their survival and propagation.
Challenges in Fern Reproduction
Predation and Disease
Threats to fern gametophytes are predation and disease, affecting the development of antheridia and archegonia. These reproductive structures are vulnerable to external factors, risking the fern's ability to reproduce successfully. Implementing protection measures is essential for ensuring optimal reproductive success.
Habitat Destruction The destruction of habitats poses significant risks to fern populations worldwide. Environmental changes impact the habitats where antheridia and archegonia develop, leading to potential disruptions in fern reproduction. Conservation efforts play a crucial role in preserving these delicate ecosystems and safeguarding fern habitats for future generations.
Conservation of Ferns
Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of fern ecosystems by ensuring genetic variation. This diversity is vital for species resilience, with antheridia and archegonia contributing significantly to this aspect. Preserving biodiversity through conservation efforts is essential for the long-term survival of fern species.
Conservation practices not only safeguard individual fern species but also contribute to the overall biodiversity within ecosystems. The presence of diverse antheridia and archegonia populations enhances the adaptability of ferns to environmental changes. Efforts aimed at preserving biodiversity help maintain the delicate balance within these ecosystems.
Conservation Efforts
Initiatives focused on conserving fern species are critical in protecting their habitats and ensuring their survival. By targeting specific habitats where antheridia and archegonia develop, conservationists can directly impact the reproductive success of ferns. Protecting these habitats is key to sustaining healthy populations of ferns in the wild.
Conservation efforts go beyond just protecting physical spaces; they also involve engaging local communities in sustainable practices. Involving communities in conservation activities not only raises awareness about the importance of preserving biodiversity but also fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility among individuals. Community participation is integral to the success of conservation programs.
Closing Thoughts
Understanding fern reproduction, from antheridia development to fertilization processes, reveals the intricate lifecycle of these ancient plants. The environmental influences and adaptive strategies showcased by ferns exemplify their resilience in the face of challenges. Conservation efforts play a vital role in preserving these unique species for future generations.
As you delve deeper into the world of ferns, consider how your actions can contribute to their conservation. Whether through supporting botanical gardens, advocating for protected habitats, or simply learning more about these fascinating plants, each step you take can make a difference in safeguarding ferns and their diverse ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where do fern antheridia develop?
Fern antheridia develop on the underside of the gametophyte, which is the heart-shaped structure. These structures are responsible for producing male gametes necessary for fertilization in ferns.
How do fern antheridia contribute to reproduction?
Fern antheridia play a crucial role in fern reproduction by producing and releasing sperm cells. These sperm cells swim through water to reach the archegonia, where they fertilize the egg, initiating the growth of a new sporophyte.
What is the significance of antheridia in the fertilization process of ferns?
Antheridia are essential in fern fertilization as they produce motile sperm cells that need water for transport to reach the egg. This process ensures successful sexual reproduction in ferns and contributes to genetic diversity within the species.
Are there any specific environmental factors that influence fern antheridia development?
Yes, environmental factors such as humidity levels, availability of water for sperm transfer, and suitable temperature can significantly impact fern antheridia development. Maintaining optimal conditions is crucial for successful fertilization and reproductive success in ferns.
How do ferns adapt their reproductive strategies to overcome challenges?
Ferns have evolved various adaptive strategies to overcome challenges in reproduction, such as producing large quantities of spores, utilizing different dispersal methods, and synchronizing reproductive processes with favorable environmental conditions. These adaptations enhance their chances of successful reproduction and survival in diverse habitats.
Image Source: Paid image from CANVA