Absolutely, ferns are a truly fascinating and ecologically important group of plants! Their presence can be traced back millions of years, and they continue to play a vital role in healthy ecosystems.
Ferns are ecosystem engineers. Their lush fronds help regulate moisture levels in the soil, preventing it from drying out too quickly. Additionally, their intricate root systems help anchor the soil, reducing erosion. This creates a healthy environment for other plants and animals to thrive. They even provide a source of food and habitat for a variety of creatures, from small insects to mammals, including trees and plants.
But that's not all! Ferns have a surprising number of uses beyond their ecological contributions. There's so much more to discover about these resilient plants, from their unique reproductive cycle to their potential uses in medicine and cultivation in the garden. Keep reading to learn more about the fascinating world of ferns!
Key Takeaways
- Understanding fern fundamentals can help appreciate their unique characteristics and importance in ecosystems.
- The vast diversity of fern species showcases their adaptability and resilience in various environments.
- Exploring fern reproduction reveals fascinating mechanisms that contribute to their survival and propagation.
- Recognizing the ecological significance of ferns highlights their role in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem balance.
- Discovering human connections to ferns demonstrates our historical, cultural, and practical relationships with these plants.
- Drawing design inspirations from ferns can lead to creative and innovative ideas in art, architecture, and landscaping.
Fern Fundamentals
Ecological Roles
Ferns stabilize soil by forming dense mats that prevent erosion, especially on slopes and riverbanks. Thriving in challenging environments, ferns contribute to ecosystem resilience by adapting to various conditions. Their presence is crucial for maintaining biodiversity as they provide habitats for a diverse range of organisms.
Ferns display a wide variety of shapes, textures, colors, and sizes, making them visually appealing in gardens and natural settings. Their unique reproduction process involves spores instead of seeds, adding to their distinctive characteristics. Dating back over 300 million years, ferns have an ancient history that showcases their enduring presence on Earth.
Unique Features
The diverse world of ferns encompasses species with striking differences in appearance, from delicate lace-like fronds to robust leathery leaves. Ferns reproduce through spores released from specialized structures called sporangia, showcasing a fascinating reproductive strategy distinct from flowering plants. This ancient group of plants has evolved over millions of years, surviving drastic environmental changes.
Life Cycle Insights
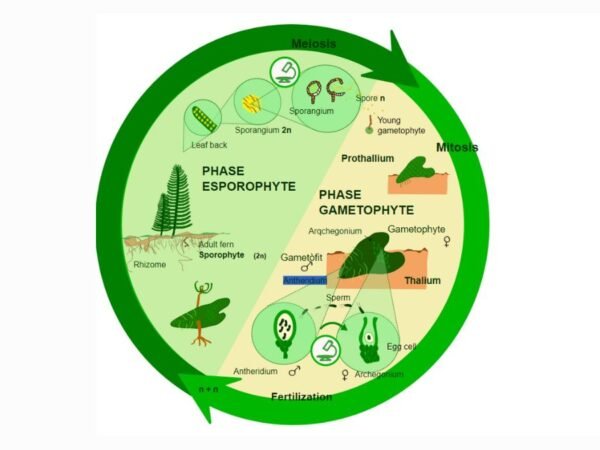
Reproduction Process
Ferns reproduce through spores that develop into tiny heart-shaped structures known as prothalli. Water plays a crucial role in the fertilization process of fern eggs, highlighting the dependency of ferns on moist environments for successful reproduction. This method differs significantly from seed-bearing plants, emphasizing the unique reproductive adaptation of ferns.
Growth Stages
From the initial stage of spore germination to the development of mature fronds, ferns undergo distinct growth stages that contribute to their ecological significance. Different fern species exhibit varying heights, with some towering tree ferns reaching impressive heights while others stay low to the ground. The diverse growth patterns of ferns play a vital role in shaping ecosystems worldwide.
Fern Diversity
Asparagus Fern
The Asparagus Fern is a popular choice for both indoor and outdoor settings due to its feathery foliage. It is often used in floral arrangements and landscaping projects. This fern species stands out with its fine, needle-like leaves that cascade elegantly.
Unlike many other fern species, the Asparagus Fern is not a true fern but belongs to the Asparagaceae family. Its unique appearance and growth habit set it apart from traditional ferns. The plant's airy and light texture adds a touch of grace to any environment.
The Asparagus Fern serves as an excellent ornamental plant, adding a lush and vibrant look to gardens, balconies, and interior spaces. Its versatility in design makes it a favorite choice for creating visually appealing landscapes.
Ostrich Fern
The Ostrich Fern boasts striking features like its large fronds resembling ostrich plumes and prefers moist woodland habitats. This fern species thrives in shady areas with rich, well-drained soil. Its distinctive appearance makes it a sought-after addition to garden landscapes.
In culinary practices, the Ostrich Fern fiddleheads are harvested as a delicacy in various cuisines worldwide. These young shoots are prized for their unique taste and nutritional value, adding flavor and texture to dishes. The fern's edible parts contribute to local food traditions.
The Ostrich Fern plays a vital role in supporting local ecosystems by providing habitat for wildlife and promoting biodiversity. Its presence in natural environments helps maintain ecological balance by offering shelter and food sources for diverse animal species.
Maidenhair Fern
The delicate fronds of the Maidenhair Fern give it an ethereal appearance, making it a favorite among gardeners and nature enthusiasts. This fern species symbolizes grace and femininity, embodying elegance with its lacy foliage. Its distinctive leaf structure sets it apart from other fern varieties.
In traditional medicine practices, the Maidenhair Fern is valued for its medicinal properties, known for treating various ailments such as respiratory issues and skin conditions. Extracts from this fern have been used for centuries in herbal remedies due to their healing properties.
The Maidenhair Fern serves as a captivating addition to landscaping projects, bringing a touch of sophistication with its graceful form and vibrant green coloration. Its aesthetic appeal enhances garden spaces, creating serene and picturesque settings ideal for relaxation.
Reproduction Unveiled
Spore Generation
Ferns reproduce through spores, tiny structures produced on the underside of their fronds. These spores are released into the environment, where they germinate and develop into new fern plants. The process of spore generation in ferns is crucial for their reproduction cycle.
Spores serve as the primary means of reproduction for ferns, allowing them to propagate and spread across different habitats. As these spores disperse, they have the potential to grow into mature fern plants, ensuring the continuity of fern species. Without spores, ferns would struggle to reproduce and thrive in various ecosystems.
The importance of spores in the survival of fern species cannot be overstated. They enable ferns to adapt to changing environmental conditions, colonize new areas, and maintain genetic diversity within populations. Spores play a vital role in sustaining the biodiversity of ferns and ensuring their long-term survival.
Lifecycle Stages
The lifecycle of ferns consists of several distinct stages, including spore germination, gametophyte development, fertilization, and sporophyte growth. Each stage plays a critical role in the overall growth and development of fern plants.
Understanding the lifecycle stages of ferns is essential for conservation efforts, as it provides insights into their reproductive strategies and ecological requirements. By studying these stages, researchers can implement effective conservation measures to protect endangered fern species and preserve their natural habitats.
The different stages in the lifecycle of ferns contribute to their resilience and ability to adapt to diverse environments. From spore dispersal to sporophyte maturation, each stage represents a key milestone in the reproductive success and ecological significance of fern plants.
Ecological Significance
Habitat Support
Ferns support diverse habitats by thriving in various environments, from forests to wetlands. They provide shelter and food for insects, birds, and small mammals. Conserving fern habitats is crucial for maintaining ecosystem health and biodiversity.
Ferns contribute to air purification through their unique leaf structures that efficiently filter pollutants. They help absorb harmful substances, enhancing air quality in both natural and indoor settings. Incorporating ferns indoors can significantly improve air quality, benefiting human health.
Soil Health
Ferns play a vital role in maintaining soil health by preventing erosion with their extensive root systems. They aid in nutrient cycling and soil stabilization, promoting overall soil fertility. Ferns also establish symbiotic relationships with soil microorganisms, further enhancing soil health.
Human Connections
Culinary Uses
Ferns have traditional culinary uses in various cultures, with certain species being consumed for their unique flavors. These ferns are known for their nutritional value, rich in vitamins and minerals. In different cuisines globally, ferns are incorporated into dishes like salads, soups, and stir-fries.
Medicinal Benefits
Specific fern species possess medicinal properties that have been utilized in traditional medicine practices for centuries. The historical use of ferns in healing remedies dates back to ancient times, where they were believed to treat various ailments. Ongoing research focuses on exploring the potential health benefits of ferns, such as anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Ornamental Value
Ferns hold significant ornamental value in gardens and landscaping due to their diverse shapes and sizes. They add texture and color to outdoor spaces, enhancing the visual appeal of landscapes. Gardeners often incorporate ferns into decorative arrangements like hanging baskets or terrariums for a touch of natural elegance.
Design Inspirations
Garden Designing
Ferns add color and texture to garden landscapes, enhancing their overall appeal. Incorporating ferns into garden design can create a lush and vibrant environment. They can be strategically placed as focal points or used as ground cover to fill in empty spaces.
When planning garden layouts, consider the various fern species available that suit different garden styles. From traditional to modern designs, ferns offer versatility in complementing diverse aesthetics. Their ability to thrive in shaded areas makes them ideal for creating unique garden compositions.
- Ferns provide a natural pop of color in gardens.
- They are excellent choices for both sunny and shaded areas.
- Ferns can be used to create visually appealing contrasts in garden designs.
Indoor Aesthetics
Indoor spaces benefit from the presence of ferns, adding a touch of nature to interior decor. The lush green foliage of ferns brings life and freshness indoors, contributing to a calming atmosphere. Indoor ferns are low maintenance plants, requiring minimal care while providing maximum visual impact.
In addition to their aesthetic value, indoor ferns play a crucial role in air purification by filtering out toxins and improving indoor air quality. Furthermore, the presence of indoor plants like ferns has been linked to reducing stress levels and promoting overall well-being.
- Indoor ferns enhance the aesthetics of living spaces.
- They require minimal care and attention.
- Ferns contribute to air purification and stress reduction indoors.
Mystery and History
Fern Folklore
Ferns have an intriguing place in historical folklore, with various myths and legends surrounding them. In some cultures, it is believed that fern seeds grant invisibility to the person carrying them. These mystical tales have sparked curiosity and fascination for centuries.
In literature and cultural beliefs, ferns are often depicted as symbols of tranquility, resilience, and even magic. They have been featured in poems, stories, and artwork as representations of growth and transformation. The enduring fascination with ferns reflects their timeless appeal across different societies.
Historical Uses
Ancient civilizations utilized ferns for a range of practical purposes, such as medicinal remedies, food sources, and even building materials. For example, Native American tribes used certain fern species for treating various ailments due to their believed healing properties. Ferns also played a role in traditional cuisines in Asia and Africa.
The cultural significance of ferns throughout history extends to rituals, ceremonies, and symbolism in many societies worldwide. In Japan, the fiddlehead fern symbolizes family unity and prosperity during the New Year celebrations. Similarly, Celtic traditions associate ferns with protection from evil spirits and luck.
Practical Guide
Growing Ferns
Growing ferns successfully involves providing the right conditions for their growth. Ensure ferns receive indirect sunlight and consistent moisture levels. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch their delicate fronds.
In different environments, adjust watering frequency based on humidity levels. Use a well-draining potting mix to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot. Monitor soil moisture regularly to maintain the ideal balance.
Common challenges in fern cultivation include pests like spider mites and scale insects. Combat these by regularly inspecting your plants and treating infestations promptly. Ensure proper air circulation to prevent fungal diseases.
Care Tips
For healthy ferns, watering is crucial. Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Adjust watering frequency based on the plant's specific needs and environmental conditions.
Different fern species have varying lighting requirements. Some prefer bright, indirect light, while others thrive in low-light conditions. Place your ferns accordingly to ensure they receive adequate light for optimal growth.
Regularly prune dead or yellowing fronds to promote new growth and maintain the plant's appearance. Over-fertilizing can harm ferns, so use a balanced liquid fertilizer sparingly during the growing season.
- Pros of Growing Ferns:
- Adds a touch of greenery and elegance to indoor spaces.
- Low maintenance plants that are relatively easy to care for.
- Cons of Growing Ferns:
- Susceptible to pests like spider mites and scale insects.
- Requires consistent monitoring of soil moisture levels for optimal growth.
Future Perspectives
Conservation Efforts
Ferns play a crucial role in biodiversity by providing habitats for various organisms and contributing to ecosystem stability. Conserving fern species is essential to maintain the delicate balance of nature. Threats such as habitat destruction, climate change, and invasive species pose significant risks to fern populations worldwide.
To combat these threats, conservation efforts are vital. Individuals can contribute by supporting protected areas, participating in habitat restoration projects, and raising awareness about the importance of ferns in ecosystems. By taking action at a local level, everyone can make a difference in preserving fern diversity for future generations.
Research Directions
Current research in fern biology and ecology focuses on understanding their unique reproductive strategies, adaptations to different environments, and interactions with other organisms. This knowledge is valuable for conservation efforts and can help identify key areas for protection.
The applications of fern research extend beyond academia. Studies on ferns have implications for medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology. For example, compounds extracted from certain fern species have shown potential medicinal properties, while others are being studied for their role in environmental remediation.
Ongoing research is crucial for uncovering the mysteries of fern diversity and ensuring their long-term survival. By investigating the ecological roles of different fern species and studying their responses to environmental changes, scientists can provide valuable insights into how best to protect these ancient plants for the future.
Closing Thoughts
In exploring the world of ferns, you've uncovered their fundamental importance, vast diversity, intriguing reproduction methods, and significant ecological roles. You've also delved into the human connections, design inspirations, mysterious history, practical gardening tips, and future perspectives surrounding these ancient plants. As you reflect on these insights, consider how ferns not only enrich ecosystems but also inspire creativity and offer a glimpse into our past while shaping our future interactions with nature.
Take this opportunity to incorporate ferns into your surroundings, whether by planting them in your garden, studying their unique features, or simply appreciating their beauty in the wild. By fostering a deeper understanding and connection with ferns, you can contribute to preserving biodiversity, promoting sustainable practices, and nurturing a sense of wonder for the natural world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are ferns important for the environment?
Ferns play a vital role in ecosystems by contributing to biodiversity, aiding in soil stabilization, and acting as habitat and food sources for various organisms. Their ability to thrive in different environments helps maintain ecological balance.
How do ferns reproduce?
Ferns reproduce through spores rather than seeds. This unique method involves the release of spores from structures called sporangia on the underside of their leaves. These spores germinate into tiny gametophytes, eventually leading to new fern plants.
What design inspirations can we draw from ferns?
The intricate patterns and shapes of fern leaves have inspired various designs in art, architecture, and fashion. From delicate fractal-like structures to graceful curves, ferns offer a wealth of inspiration for creative endeavors seeking organic and elegant aesthetics.
How do humans connect with ferns?
Humans have historically utilized ferns for medicinal purposes, food sources, and ornamental plantings. Cultural significance in folklore and rituals has further deepened the connection between humans and ferns throughout history.
What future perspectives exist regarding fern conservation?
As awareness of biodiversity importance grows, efforts to conserve fern species are increasing. Conservation strategies involve habitat protection, restoration projects, and research on threatened species to ensure the preservation of these ancient plants for future generations.
Image Source: Paid image from CANVA